Difference between revisions of "Figure 3.2: Illustration of a state model"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{Figure |Chapter=System Modeling |Figure number=3.2 |Figure title=Illustration of a state model |GitHub URL=https://github.com/murrayrm/fbs2e-python/blob/main/figure-3.2-stat...") |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|Chapter=System Modeling | |Chapter=System Modeling | ||
|Figure number=3.2 | |Figure number=3.2 | ||
| + | |Sort key=302 | ||
|Figure title=Illustration of a state model | |Figure title=Illustration of a state model | ||
|GitHub URL=https://github.com/murrayrm/fbs2e-python/blob/main/figure-3.2-state_model.py | |GitHub URL=https://github.com/murrayrm/fbs2e-python/blob/main/figure-3.2-state_model.py | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[Image:figure-3.2-state_model.png]] | + | [[Image:figure-3.2-state_model.png|640px]] |
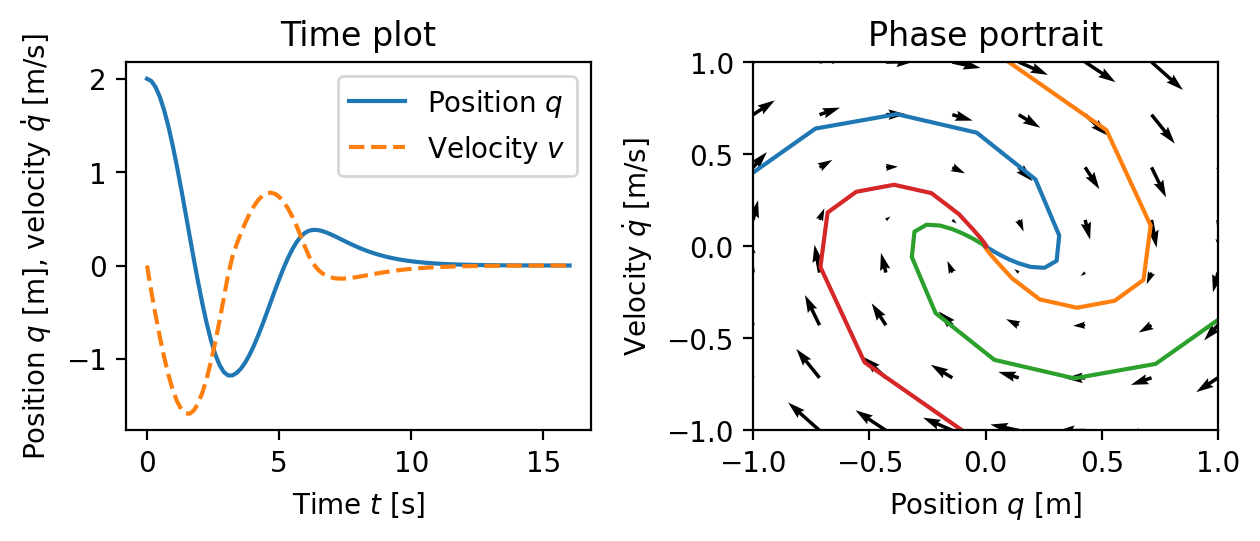
'''Figure 3.2''': Illustration of a state model. A state model gives the rate of change of the state as a function of the state. The plot on the left shows the evolution of the state as a function of time. The plot on the right, called a phase portrait, shows the evolution of the states relative to each other, with the velocity of the state denoted by arrows. | '''Figure 3.2''': Illustration of a state model. A state model gives the rate of change of the state as a function of the state. The plot on the left shows the evolution of the state as a function of time. The plot on the right, called a phase portrait, shows the evolution of the states relative to each other, with the velocity of the state denoted by arrows. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 36: | ||
# | # | ||
# The nonlinear damping is implemented as a change in the linear damping | # The nonlinear damping is implemented as a change in the linear damping | ||
| − | # coefficient at a small velocity. This is intended to roughly correspond | + | # coefficient at a small velocity. This is intended to roughly correspond |
| − | # to some sort of stiction (and give an interesting phase portrait). The | + | # to some sort of stiction (and give an interesting phase portrait). The |
# default parameters for the system are given by | # default parameters for the system are given by | ||
# | # | ||
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
# This corresponds to a fairly lightly damped oscillator away from the origin. | # This corresponds to a fairly lightly damped oscillator away from the origin. | ||
| − | def | + | def _nlspringmass(t, x, u, params): |
| + | m = params.get('m', 1) | ||
| + | k = params.get('k', 1) | ||
| + | b1 = params.get('b1', 2) | ||
| + | b2 = params.get('b2', 0.01) | ||
| + | dth = params.get('dth', 0.2) | ||
| + | |||
# Compute the friction force | # Compute the friction force | ||
if abs(x[1]) < dth: | if abs(x[1]) < dth: | ||
| Line 60: | Line 67: | ||
# Return the time derivative of the state | # Return the time derivative of the state | ||
return np.array([x[1], -k/m * x[0] - Fb/m]) | return np.array([x[1], -k/m * x[0] - Fb/m]) | ||
| + | nlspringmass = ct.nlsys(_nlspringmass, None, states=2, inputs=0, outputs=2) | ||
# | # | ||
| Line 67: | Line 75: | ||
t = np.linspace(0, 16, 100) | t = np.linspace(0, 16, 100) | ||
| − | + | resp = ct.input_output_response(nlspringmass, t, 0, [2, 0]) | |
| + | y = resp.outputs | ||
| − | plt.plot(t, y[ | + | plt.plot(t, y[0], '-', t, y[1], '--') |
plt.xlabel('Time $t$ [s]') | plt.xlabel('Time $t$ [s]') | ||
| − | plt.ylabel('Position $q$ [m], velocity $\dot q$̇ [m/s]') | + | plt.ylabel(r'Position $q$ [m], velocity $\dot q$̇ [m/s]') |
plt.title('Time plot') | plt.title('Time plot') | ||
plt.legend(['Position $q$', 'Velocity $v$']) | plt.legend(['Position $q$', 'Velocity $v$']) | ||
| Line 78: | Line 87: | ||
# (b) Generate a phase plot for the damped oscillator | # (b) Generate a phase plot for the damped oscillator | ||
# | # | ||
| − | plt.subplot(2, 2, 2) | + | ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 2) |
| − | ct. | + | cplt = ct.phase_plane_plot( |
nlspringmass, # dynamics | nlspringmass, # dynamics | ||
| − | + | [-1, 1, -1, 1], # bounds of the plot | |
| − | + | gridspec=[8, 8], # number of points for vectorfield | |
| − | + | plot_vectorfield=True, # plot vectorfield | |
| + | plot_streamlines=False, # plot streamlines separately | ||
| + | plot_separatrices=False, # leave off separatrices | ||
| + | ax=ax | ||
| + | ) | ||
| + | ct.phaseplot.streamlines( # Plot streamlines from selected points | ||
| + | nlspringmass, | ||
| + | np.array([[-1, 0.4], [0.1, 1], [1, -0.4], [-0.1, -1]]), | ||
| + | 10, ax=ax | ||
| + | ) | ||
plt.xlabel('Position $q$ [m]') | plt.xlabel('Position $q$ [m]') | ||
| − | plt.ylabel('Velocity $\dot q$ [m/s]') | + | plt.ylabel(r'Velocity $\dot q$ [m/s]') |
plt.title('Phase portrait') | plt.title('Phase portrait') | ||
plt.axis([-1, 1, -1, 1]) | plt.axis([-1, 1, -1, 1]) | ||
Latest revision as of 18:34, 16 November 2024
| Chapter | System Modeling |
|---|---|
| Figure number | 3.2 |
| Figure title | Illustration of a state model |
| GitHub URL | https://github.com/murrayrm/fbs2e-python/blob/main/figure-3.2-state model.py |
| Requires | python-control |
Figure 3.2: Illustration of a state model. A state model gives the rate of change of the state as a function of the state. The plot on the left shows the evolution of the state as a function of time. The plot on the right, called a phase portrait, shows the evolution of the states relative to each other, with the velocity of the state denoted by arrows.
# figure-3.2-state_mode.py - illustration of a state model
# RMM, 2 Jul 2021
#
# Figure 3.2: Illustration of a state model. A state model gives the rate of
# change of the state as a function of the state. The plot on the left shows
# the evolution of the state as a function of time. The plot on the right,
# called a phase portrait, shows the evolution of the states relative to
# each other, with the velocity of the state denoted by arrows.
#
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import control as ct
#
# Spring mass system with nonlinear dampling
#
# This function gives the dynamics for a dampled oscillator with nonlinear
# damping. The states of the system are
#
# x[0] position
# x[1] velocity
#
# The nonlinear damping is implemented as a change in the linear damping
# coefficient at a small velocity. This is intended to roughly correspond
# to some sort of stiction (and give an interesting phase portrait). The
# default parameters for the system are given by
#
# m = 1 mass, kg
# k = 1 spring constant, N/m
# b1 = 1 damping constant near origin, N-sec/m
# b2 = 0.01 damping constant away from origin, N-sec/m
# dth = 0.5 threshold for switching between damping
#
# This corresponds to a fairly lightly damped oscillator away from the origin.
def _nlspringmass(t, x, u, params):
m = params.get('m', 1)
k = params.get('k', 1)
b1 = params.get('b1', 2)
b2 = params.get('b2', 0.01)
dth = params.get('dth', 0.2)
# Compute the friction force
if abs(x[1]) < dth:
Fb = b1 * x[1];
elif x[1] < 0:
Fb = -b1 * dth \
+ b2 * (x[1] + dth);
else:
Fb = b1 * dth \
+ b2 * (x[1] - dth);
# Return the time derivative of the state
return np.array([x[1], -k/m * x[0] - Fb/m])
nlspringmass = ct.nlsys(_nlspringmass, None, states=2, inputs=0, outputs=2)
#
# (a) Simulation of the nonlinear spring mass system
#
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
t = np.linspace(0, 16, 100)
resp = ct.input_output_response(nlspringmass, t, 0, [2, 0])
y = resp.outputs
plt.plot(t, y[0], '-', t, y[1], '--')
plt.xlabel('Time $t$ [s]')
plt.ylabel(r'Position $q$ [m], velocity $\dot q$̇ [m/s]')
plt.title('Time plot')
plt.legend(['Position $q$', 'Velocity $v$'])
#
# (b) Generate a phase plot for the damped oscillator
#
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
cplt = ct.phase_plane_plot(
nlspringmass, # dynamics
[-1, 1, -1, 1], # bounds of the plot
gridspec=[8, 8], # number of points for vectorfield
plot_vectorfield=True, # plot vectorfield
plot_streamlines=False, # plot streamlines separately
plot_separatrices=False, # leave off separatrices
ax=ax
)
ct.phaseplot.streamlines( # Plot streamlines from selected points
nlspringmass,
np.array([[-1, 0.4], [0.1, 1], [1, -0.4], [-0.1, -1]]),
10, ax=ax
)
plt.xlabel('Position $q$ [m]')
plt.ylabel(r'Velocity $\dot q$ [m/s]')
plt.title('Phase portrait')
plt.axis([-1, 1, -1, 1])
plt.tight_layout()