Cruise control
This page documents the cruise control system that is used as a running example throughout the text. A detailed description of the dynamics of this system are presented in Chapter 4 - Examples. This page contains a description of the system, including the models and commands used to generate some of the plots in the text.
Introduction
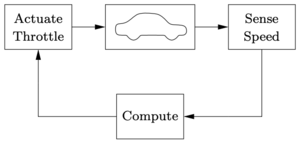
Cruise control is the term used to describe a control system that regulates the speed of an automobile. Cruise control was commercially introduced in 1958 as an option on the Chrysler Imperial. The basic operation of a cruise controller is to sense the speed of the vehicle, compare this speed to a desired reference, and then accelerate or decelerate the car as required. The figure to the right shows a block diagram of this feedback system.
A simple control algorithm for controlling the speed is to use a "proportional plus integral" feedback. In this algorithm, we choose the amount of gas flowing to the engine based on both the error between the current and desired speed, and the integral of that error. The plot on the right shows the results of this feedback for a step change in the desired speed and a variety of different masses for the car (which might result from having a different number of passengers or towing a trailer). Notice that independent of the mass (which varies by 25% of the total weight of the car), the steady state speed of the vehicle always approaches the desired speed and achieves that speed within approximately 10-15 seconds. Thus the performance of the system is robust with respect to this uncertainty.
Dynamic model
To develop a mathematical model we start with a force balance for the car body. Let Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v} be the speed of the car, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m} the total mass (including passengers), Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F} the force generated by the contact of the wheels with the road, and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_\text{d}} the disturbance force due to gravity, friction and aerodynamic drag. The equation of motion of the car is simply
The force Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F} is generated by the engine, whose torque is proportional to the rate of fuel injection, which is itself proportional to a control signal Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0 \leq u \leq 1} that controls the throttle position. The torque also depends on engine speed Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega} . A simple representation of the torque at full throttle is given by the torque curve
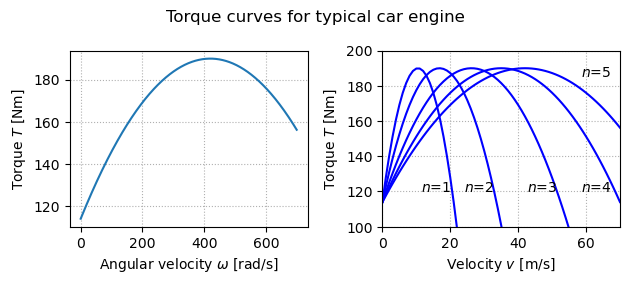
where the maximum torque Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_\text{m}} is obtained at engine speed Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_\text{m}} . Typical parameters are Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_m = 190} Nm, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_m} = 420 rad/s (about 4000 RPM) and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = 0.4} .
Let Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} be the gear ratio and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} the wheel radius. The engine speed is related to the velocity through the expression
and the driving force can be written as
Typical values of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_n} for gears 1 through 5 are Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_1 = 40} , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_2 = 25} , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_3 = 16} , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_4 = 12} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_5 = 10} . The inverse of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_n} has a physical interpretation as the effective wheel radius. The figure to the right shows the torque as a function of vehicle speed. The figure shows that the effect of the gear is to "flatten" the torque curve so that an almost full torque can be obtained almost over the whole speed range.
The disturbance force Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_\text{d}} has three major components: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_\text{g}} , the forces due to gravity; Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_\text{r}} , the forces due to rolling friction; and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_\text{a}} , the aerodynamic drag. Letting the slope of the road be Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta} , gravity gives the force Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_\text{g} = m g \sin\theta} , where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g = 9.8\, \text{m}/\text{s}^2} is the gravitational constant. A simple model of rolling friction is
where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_\text{r}} is the coefficient of rolling friction and sgn(Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v} ) is the sign of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v} or zero if Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v = 0} . A typical value for the coefficient of rolling friction is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_\text{r} = 0.01} . Finally, the aerodynamic drag is proportional to the square of the speed:
where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho} is the density of air, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_d} is the shape-dependent aerodynamic drag coefficient and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} is the frontal area of the car. Typical parameters are Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho = } 1.3 k/mFailed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {}^3} , Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_\text{d} = 0.32} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A =} 2.4 mFailed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {}^2} .
Python model
The model for the system above can be built using the Python Control Toolbox. The code blocks in this section can be used to generate the plots above.
def vehicle_update(t, x, u, params={}):
"""Vehicle dynamics for cruise control system.
Parameters
----------
x : array
System state: car velocity in m/s
u : array
System input: [throttle, gear, road_slope], where throttle is
a float between 0 and 1, gear is an integer between 1 and 5,
and road_slope is in rad.
Returns
-------
float
Vehicle acceleration
"""
from math import copysign, sin
sign = lambda x: copysign(1, x) # define the sign() function
# Set up the system parameters
m = params.get('m', 1600.) # vehicle mass, kg
g = params.get('g', 9.8) # gravitational constant, m/s^2
Cr = params.get('Cr', 0.01) # coefficient of rolling friction
Cd = params.get('Cd', 0.32) # drag coefficient
rho = params.get('rho', 1.3) # density of air, kg/m^3
A = params.get('A', 2.4) # car area, m^2
alpha = params.get(
'alpha', [40, 25, 16, 12, 10]) # gear ratio / wheel radius
# Define variables for vehicle state and inputs
v = x[0] # vehicle velocity
throttle = np.clip(u[0], 0, 1) # vehicle throttle
gear = u[1] # vehicle gear
theta = u[2] # road slope
# Force generated by the engine
omega = alpha[int(gear)-1] * v # engine angular speed
F = alpha[int(gear)-1] * motor_torque(omega, params) * throttle
# Disturbance forces
#
# The disturbance force Fd has three major components: Fg, the forces due
# to gravity; Fr, the forces due to rolling friction; and Fa, the
# aerodynamic drag.
# Letting the slope of the road be \theta (theta), gravity gives the
# force Fg = m g sin \theta.
Fg = m * g * sin(theta)
# A simple model of rolling friction is Fr = m g Cr sgn(v), where Cr is
# the coefficient of rolling friction and sgn(v) is the sign of v (±1) or
# zero if v = 0.
Fr = m * g * Cr * sign(v)
# The aerodynamic drag is proportional to the square of the speed: Fa =
# 1/2 \rho Cd A |v| v, where \rho is the density of air, Cd is the
# shape-dependent aerodynamic drag coefficient, and A is the frontal area
# of the car.
Fa = 1/2 * rho * Cd * A * abs(v) * v
# Final acceleration on the car
Fd = Fg + Fr + Fa
dv = (F - Fd) / m
return dv
def motor_torque(omega, params={}):
# Set up the system parameters
Tm = params.get('Tm', 190.) # engine torque constant
omega_m = params.get('omega_m', 420.) # peak engine angular speed
beta = params.get('beta', 0.4) # peak engine rolloff
return np.clip(Tm * (1 - beta * (omega/omega_m - 1)**2), 0, None)
vehicle = ct.NonlinearIOSystem(
vehicle_update, None, name='vehicle',
inputs = ('u', 'gear', 'theta'), outputs = ('v'), states=('v'))
# Figure 4.2a - single torque curve as function of omega
omega_range = np.linspace(0, 700, 701)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.plot(omega_range, [motor_torque(w) for w in omega_range])
plt.xlabel('Angular velocity $\omega$ [rad/s]')
plt.ylabel('Torque $T$ [Nm]')
plt.grid(True, linestyle='dotted')
# Figure 4.2b - torque curves in different gears, as function of velocity
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
v_range = np.linspace(0, 70, 71)
alpha = [40, 25, 16, 12, 10]
for gear in range(5):
omega_range = alpha[gear] * v_range
plt.plot(v_range, [motor_torque(w) for w in omega_range],
color='blue', linestyle='solid')
# Set up the axes and style
plt.axis([0, 70, 100, 200])
plt.grid(True, linestyle='dotted')
# Add labels
plt.text(11.5, 120, '$n$=1')
plt.text(24, 120, '$n$=2')
plt.text(42.5, 120, '$n$=3')
plt.text(58.5, 120, '$n$=4')
plt.text(58.5, 185, '$n$=5')
plt.xlabel('Velocity $v$ [m/s]')
plt.ylabel('Torque $T$ [Nm]')
plt.suptitle('Torque curves for typical car engine');
plt.tight_layout()
Exercises
The following exercises make use of the cruise control model described here:
Further Reading
- How Stuff Works: cruise control
- Wikipedia: cruise control